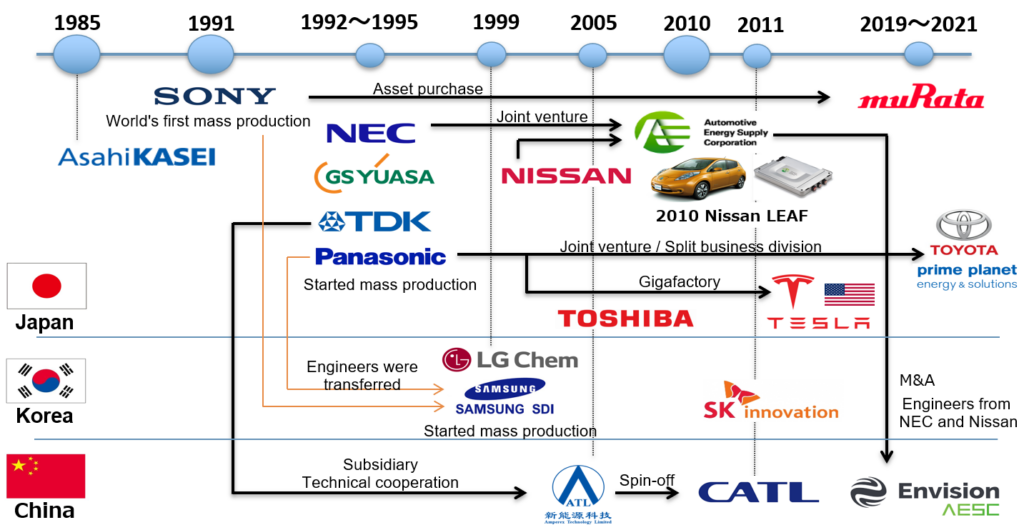
In 1985 a team around Akira Yoshino from the Japanese Asahi Kasei Corporation finished the development of a lithium ion battery that allowed for commercial mass production and that was the prototype of the lithium ion battery which we know today. Further developments followed in Japan and later also in South Korea and China, resulting in this part of Asia becoming the leading geographical region of the lithium ion battery industry.
HIOKI and Lithium Ion Batteries
Just one year later, in October 1986, HIOKI launched an instrument that allowed for these lithium ion batteries to be tested in production. Just one year later? Sounds like a very short time to market – even considering that Japanese engineers have the reputation of spending most of the day at work. Can you imagine to develop, industrialize, test and produce a new and reliable test instrument within one year? No. So, how did they do it?
The “HIOKI 3225” was actually not called a battery tester at the time but an “AC MilliOhm Tester” which derived from the measurement principle where a very small AC test signal is injected into the DUT to measure it’s (AC) resistance. This was not the first MilliOhm tester from HIOKI – there already was a “HIOKI 3220” as well as a “HIOKI 3224” before. So when news of the first commercially viable lithium ion battery broke in 1985, HIOKI already had an instrument with a suitable measurement principle in the making.
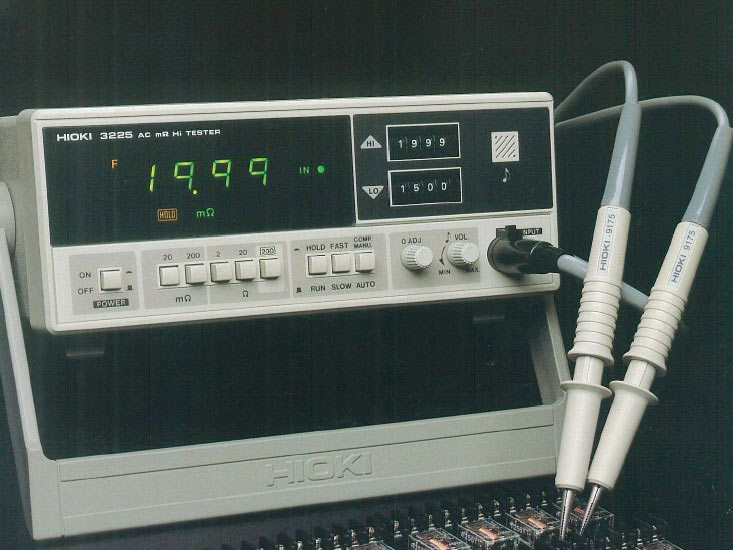
The new feature in the 3225 was that it could handle DUTs with a DC potential (like a battery) – something it’s predecessors where not able to. This made the HIOKI 3225 the first HIOKI battery tester – and as you can see in the above image the smallest range was just 20 mOhm.

For HIOKI, the 3225 was an important instrument to start supplying measurement products and solutions to the battery manufacturing industry. Not only are the successors of the 3225 widely known and used – with the BT3562 having basically become a standard product in this industry. HIOKI now also supplies resistance meters like the RM2610 or the RM3545 to the battery industry, as well as insulation testers (e.g. ST5520), high precision volt meters (DM7276) and special impedance measurement instruments like the BT4560 or the IM3590.
Find out more how HIOKI can help with your battery test & measurement requirements by contacting one of HIOKI’s sales partners – or just simply by getting in touch with me.